Photo by Vlad Tchompalov on Unsplash
THE NEED FOR SEMICONDUCTORS IN AUTOMOTIVE
The automotive industry is going through a significant transformation. Countries all over the world are pressing for greener and eco-friendly vehicles. Government policies are getting stricter and demand vehicular technologies that require smarter software and hardware.
The de-facto transformation is towards electric vehicles. However, other vehicular technologies (hybrid, autonomous, and alternate-fuel) are also driving the change in the automotive industry, and all this is pushing automotive companies to innovate. To keep up with the smart and safe automotive features, the share of software and hardware in automotive is increasing tremendously, thus leading to new automotive technology companies are also emerging. The emerging automotive companies work in collaboration with the established automotive companies or are launching their own smarter electric, hybrid, autonomous, and alternate-fuel automotive products.
One of the pieces to make electric, hybrid, autonomous and alternate-fuel vehicles are semiconductor products, as it forms the base for the hardware required to run the software. In 2021, automotive production may be impacted due to the shortage of semiconductor chips, and it shows the dependency the automotive industry has on the semiconductor industry.
The Semiconductor Industry And Products Are Key To Developing Smarter Hardware To Drive The Automotive Industry Using Smarter Software
The need for semiconductor solutions in automotive is also pushing the innovation and development of smarter automotive chips to drive vehicles safely. The increasing need to develop error-prone software that runs on efficient hardware is vital and is driving the automotive industry to re-invent automotive solutions from a semiconductor point of view.
It is not that semiconductor products started getting used by the automotive industry in 2020. The automotive industry has relied on semiconductor products for decades. From airbags to infotainment and many other solutions have always required defect-free semiconductor products. However, the landscape of semiconductors in automotive is changing from individual silicon components to more centralized silicon systems. The semiconductor products work excellent for solo operations.
However, when the goal is to connect the system for level 5 autonomy or increasing hybrid efficiency, a centralized automotive-specific system-on-a-chip (SoC) is required. The centralized automotive semiconductor-based solution still relies on individual semiconductor components and is leading to innovative work from both the established automotive firms and the new semiconductor FAB-LESS companies looking to eat into the automotive and semiconductor market.
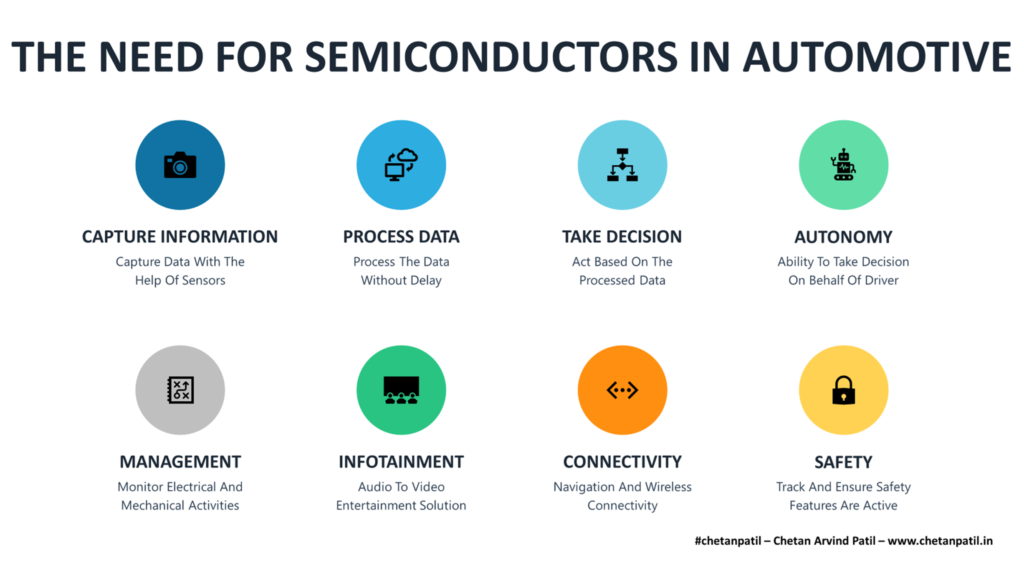
A centralized silicon system needs to cater to the following uses cases for autonomous automotive solution:
Capture Information: Ability to capture information with the help of monitoring sensors, LIDAR, and RADAR
Process Data: Information captured should is processed without delay
Take Decision: The processed data is used to take accurate actions
Autonomy: Decide on behalf of the driver to enable a safer experience
Management: Track electrical and mechanical activities to provide vehicle health
Infotainment: Display, audio, and video system for entertainment
Connectivity: On-the-go navigation, Bluetooth, 5G, and WiFi connectivity
Safety: Ensure critical components and features are working and alert when maintenance is required
The above use cases of semiconductors are valid for any kind of two/three/four automotive solution, including passenger, commercial, motorcycles, and industrial automobiles.
Developing semiconductor solutions for automotive requires strong collaboration with the semiconductor design and manufacturing industry. In some cases, the semiconductor solutions are also being developed in-house by automotive companies. It is why the automakers are investing or building R&D facilities to come up with a high precision silicon need for future vehicles.
THE DEVELOPMENT OF SEMICODUCTORS IN AUTOMOTIVE
It is critical to make use of a high-level intelligence system to make automotive products smarter. The growing share of technology-powered features in modern vehicles is prompting the automotive industry to invest in software and hardware capabilities in-house. In many cases, automotive companies are also collaborating and investing by out-sourcing many of the vital semiconductor solutions from silicon chips to sensors systems.
Automotive giants and the silicon chip:
BMW: To remove its dependency on outsourced power semiconductor products, BMW has invested in GaN semiconductor startup. In parallel, BMW has also collaborated with Intel to drive its fully autonomous vehicle project.
BOSCH: Like DENSO, BOSCH has been the provider and one of the leaders of automotive components. Given the growth of alternate fuel technology and the dependency on semiconductor products, BOSCH has upped its ante and in-course grabbed billions of vehicle computer orders. BOSCH is also one of the rare automotive companies to also own semiconductor FABs, and this puts BOSCH in a unique position to not only design in-house but also manufacture. Recently, BOSCH also launched a new chip that promises to be a game-changer navigation technology.
DENSO: While DENSO is party owned by Toyota, it still does a lot of work on its own to power future automotive technologies. In line with its ambitions to power EVs, DENSO has invested in startups focusing on semiconductor solutions to manage power and performance. On other hand, DENSO has also taken equity in Infineon Technologies to enhance its semiconductor portfolio. It has also formed a new semiconductor called MIRISE Technologies in-collaboration with Toyota, to develop next-generation in-vehicle semiconductors.
Daimler: To compete with Tesla and other automotive companies, Daimler has partnered with Nvidia to speed up its use of next-generation silicon chips. Apart from this, Daimler has also increased investment in battery manufacturing. An interesting fact – In 1997 Daimler-Benz AG sold its semiconductor business unit TEMIC Telefunken Microelectronic GmbH to Vishay Intertechnology and now it is going back to the same business area to survive the growing semiconductor in the automotive products.
Ford: To cater to its elective vehicle and autonomous technologies, Ford is working with Mobileye and Intel to drive its semiconductor needs.
Hyundai: Hyundai has a long-term plan to remove the dependency on automotive products. In line with its vision, Hyundai has launched a semiconductor lab to develop semiconductor products for electric/hybrid vehicle powertrain controllers.
Honda: Honda a decade ago invested in Shindengen Electric Manufacturing. Given how big Honda is in the two-wheeler segment and the growing electric vehicles market, Honday can reap the benefits of the strategic investment made in Shindengen Electric.
Nissan: Nissan has collaborated with Renesas for its innovative semiconductor needs.
NXP: NXP Semiconductor is one of the leaders in automotive solutions. Apart from a strong portfolio and design capabilities, NXP has an advantage in its manufacturing expertise in automotive products. The growing line of products for automotive will certainly make NXP stand out in the market.
Toyota: Since 2014, Toyota has been using innovative semiconductor technologies to enable higher-fuel efficiency. Last year, Toyota formed JV with DENSO to focus on in-house silicon chip development due to the exploding cost of semiconductors in automotive.
Tata Motors: Tata is one of the leaders in passenger and commercial vehicles in India. Its semiconductor arm Tata ELXSI is capable of providing all the required semiconductor solutions for its need apart from its decade-long collaboration with other automotive semiconductor product providers.
Volkswagen: A few years ago, Volkswagen formed a deep partnership with Infineon Technologies to drive its TRANSFORM 2025+ strategy in line with semiconductors in automotive.
There are numerous examples of big automotive giants already owning or investing in semiconductor chip development. Given the decreasing cost of developing an automotive solution using advanced intelligence techniques, several startups and newcomers are also shaking the automotive market by providing semiconductor solutions.
New comers in automotive silicon chip:
Autotalks: A FAB-LESS startup providing semiconductor solutions for vehicle-to-everything (V2X) communications for the automotive industry.
Apple: Not official yet, but there are numerous reports of Apple’s electric car. If that happens, it is for sure going to be an in-house development.
Argo AI: Developing its software to hardware self-driving technology, Argo AI is another startup getting into automotive semiconductors. It also got recently merged with Audi’s AI center.
GEO Semiconductor: A FAB-LESS semiconductor startup that is providing integrated circuits (ICs) for video and geometry processing.
indie semiconductor: indie Semiconductor makes SoCs for the automotive industry. It has changed its portfolio in the last few years but has certainly got a front foot in the connected car and infotainment business.
NIO: NIO is a China-based EV maker that has decided to go big for in-house silicon chip development to fulfill its need for semiconductors.
NIKOLA: NIKOLA is another promising automotive company. It has been focusing on designing and manufacturing electrical components for greener vehicles. So far, NIKOLA has focused on semi and soon plans to venture into the passenger segment.
SLD Laser: Started in 2013, SLD Laser is pushing the development of laser-based sensor solutions for the automotive industry.
Silicon Mobility: Founded in 2015, Silicon Mobility is providing a semiconductor-based mobility solution to make EV more efficient.
Tesla: While Tesla is not new to the automotive market, its silicon solution is certainly is. It aims to provide a silicon sandbox that is going to make any vehicle an autonomous one. Tesla AI chip is still under in-house use, but will certainly open up the market if sold separately.
Waymo: Owned by Google, Waymo, for now, is using Intel’s technology but in-house is also planning to develop its silicon chip.
Zoox: Amazon bought Zoox early this year and also unveiled its self-driving car. With Amazon’s experience in developing hardware via Amazon Lab126, Zoox automotive hardware solution will be innovative.
The list of newcomers and startups in automotive semiconductors is going to increase. It will be interesting to see how the semiconductors market adapts to the solutions from the smaller companies.
It is for sure going to increase the importance of semiconductor design and development. However, there are still major challenges to overcome before automotive companies can make it big in the semiconductor industry.
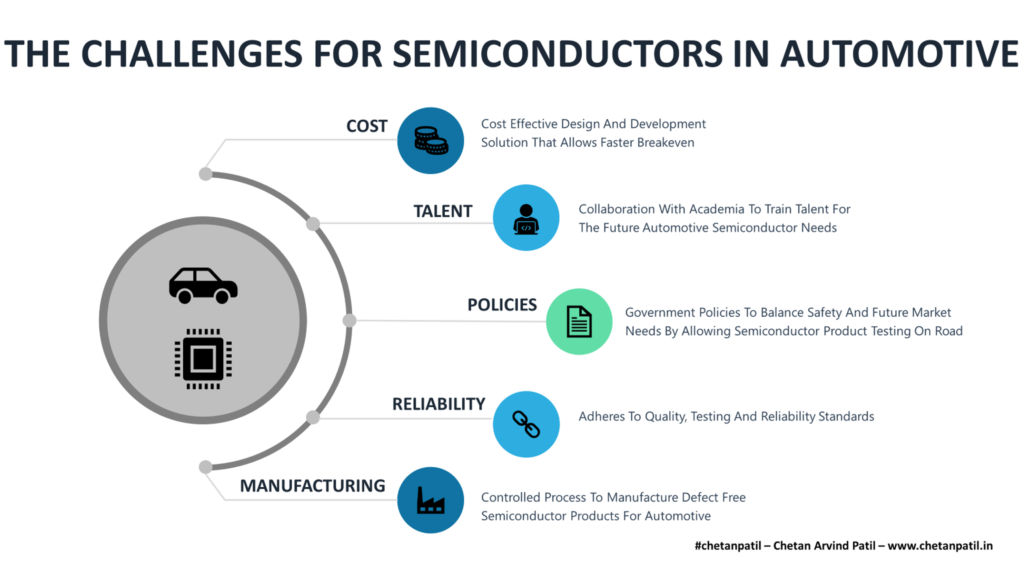
THE CHALLENGES FOR SEMICONDUCTORS IN AUTOMOTIVE
Automotive companies which have been in the industry can establish the semiconductor business unit to meet its need. The challenges arise for newcomers wanting to cater to the automotive industry.
Five major challenges might hinder the progress of newcomers from providing elegant automotive semiconductor solutions:
Cost: Even though the share of semiconductor cost in new vehicles is on the rise, the challenge remains on optimizing the development and manufacturing cost to reach the breakeven point. Optimizing the process to make a low-cost product for large scale consumption is still a challenge. On top of it, proving the smarter semiconductor driven solution to the market is getting tougher. Autonomous (not specifically self-driving) technologies take years to test on the road before they can be used by the mass market. All this adds to the cost.
Talent: Acquiring relevant software and hardware talent to bring silicon solutions to bring innovation to the market is another challenge. Automotive companies getting into self-driving, electric vehicles, and alternate-fuel solutions are doing all they can to form the best team. In some cases, the practice is not as per everyone’s liking. Bringing new talents on-board and training them takes years too. Challenges also remain with universities to launch programs that cater to the new-age automotive and semiconductor market that requires different skills and demands. An interdisciplinary study that combines mechanical, computer, electrical, and semiconductor engineering is the need of the hour.
Policies: The lives of many on the road are at stake, and Government policies play a crucial role in the automotive industry. Not all countries or states enable the framework to test autonomous solutions out on the road. Dedicated infrastructure is required to test solutions like lane guidance and autonomous driving. It is difficult for states to grant permission to test the solution on public roads due to dangerous un-known consequences. Only a few examples of how state policy can strike the balance of technological progress and road safety. Arizona is one such example. The policy has to lead Chalder in Arizona to become the hub for self-driving design and development. Waymo to Uber to Cruise are all testing their solutions out on the road. It shows the growing need to make policies that strike the balance of safety and future market needs.
The Semiconductor Automotive Product Development Demands Talent Pool Trained With Interdisciplinary Curriculum Covering Mechanical, Computer, Electrical And Semiconductor Engineering.
Reliability: Semiconductor automotive products have to go through stringent qualification, testing, and reliability criteria. Automotive Electronics Council (AEC) and a few other standards provide the guidelines for qualifying the semiconductor products. The guidelines require the temperature to reliability stress testing. All these require resources, time, cost, and talent to execute. A chip not functioning during a crash can lead to fatality. Making automotive semiconductor product reliable is a key concern.
Manufacturing: Automotive semiconductor products eventually have to get manufactured in the same arena where smartphone semiconductor products get manufactured. A semiconductor FAB and OSAT have to ensure strict control over the process to ensure zero variation between lots of the same product. Controlling such requirement demands strong industry flow that enables defect-free products. FAB-LESS companies developing semiconductor products for the automotive industry have to engage and invest with semiconductor manufacturing teams.
The challenges are many, but so are the opportunities. Companies have to increase focus on semiconductor products in the automotive industry at the chip level. The automotive industry has leverage semiconductor solutions for decades.
The next decade is going to be a game-changer. The share of semiconductor products and costs in automotive is only going to quadruple. All this will open tremendous opportunities both for the semiconductor and the automotive industry.