Image Generated Using 4o
AI As A Creative Partner In Chip Design
Chip design has always been a demanding discipline, requiring engineers to balance performance, power, and area across endless iterations. Traditionally, much of this work has been manual and time-consuming. With the rise of large language models, engineers now have intelligent collaborators at their side.
Recent research demonstrates how these models can take natural language specifications, such as “design a 4-bit adder,” and generate corresponding Verilog code that is both syntactically correct and functionally accurate.
Projects like VerilogEval and RTLLM highlight how LLMs can handle structured hardware description, while experiments such as ChipGPT allow engineers to ask why a module fails verification and receive context-aware debugging suggestions.
These capabilities are not about replacing human designers, but about extending their reach. The engineer provides intent and creative direction, while AI manages repetitive exploration, expanding the possibilities of what can be achieved in each design cycle.
Flexible Architectures For A Rapidly Evolving Landscape
The impact of AI co-creativity extends beyond the design process into the way chips themselves are architected. Traditional fixed-function hardware often struggles to remain relevant as AI models evolve, since a design optimized for one generation of algorithms may quickly become outdated.
AI-enabled frameworks such as AutoChip and HiVeGen are addressing this challenge by automatically generating modular and reconfigurable hardware. Instead of starting over for each new workload, AI adapts existing modules to meet new requirements.
This makes it possible to create architectures that behave more like flexible platforms than static end products, evolving alongside the software they are built to support.
Such adaptability reduces the risk of obsolescence, lowers redesign costs, and ensures that semiconductors keep pace with the rapid cycles of algorithmic change.
Why AI Co-Creativity Matters
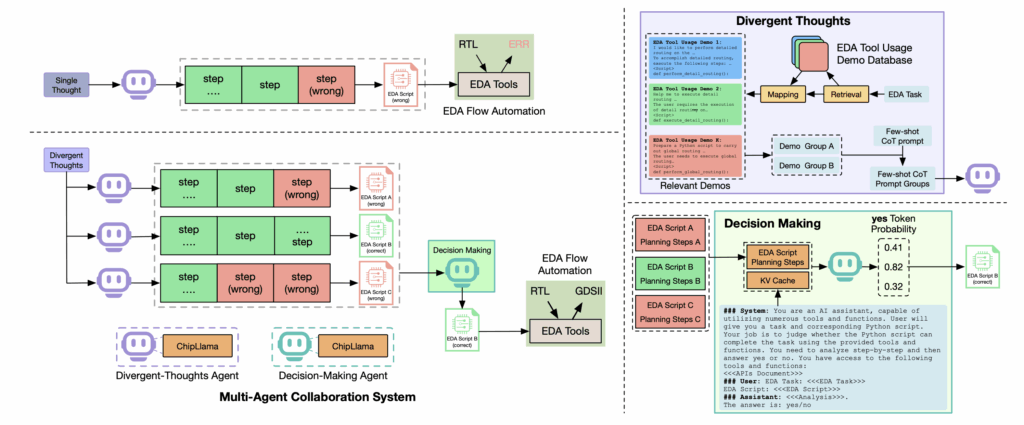
The practical benefits of AI as a co-creator are felt across the entire productization cycle. Multi-agent systems such as AutoEDA demonstrate that large portions of the RTL-to-GDSII flow can be automated, with agents specializing in tasks like synthesis, placement, and verification before combining their results into a complete design.
By mirroring the way human teams distribute responsibilities, these systems drastically shorten time-to-market. Designs that once took months to finalize can now be completed in weeks, allowing faster response to industry demands.
Quality also improves when AI is embedded in the flow. Benchmarks such as CorrectBench illustrate that LLMs are capable of generating verification testbenches with high functional coverage, reducing the burden on engineers and improving design reliability. Similarly, AI-driven defect detection in layout generation helps identify issues early in the process, preventing costly downstream corrections.
These capabilities enable engineers to concentrate on strategic architectural decisions and system-level innovation, knowing that AI can handle the lower-level repetitive work.
An Expanding Ecosystem Of Co-Creativity
The reach of AI is spreading across the semiconductor ecosystem. Conversational assistants like LLM-Aided allow engineers to interact with tools in natural language, reducing the steep learning curve often associated with complex design environments.
Code and script generation tools, such as those explored in ChatEDA, EDAid, and IICPilot, produce automation scripts for synthesis and verification, eliminating the need for repetitive manual scripting.
Multi-agent frameworks go further, creating distributed AI systems in which specialized agents collaborate to carry an entire design from high-level specification to implementation.
These developments point toward an ecosystem where human engineers and AI systems are intertwined at every stage of productization. Instead of siloed and linear workflows, semiconductor development becomes a dynamic collaboration in which human creativity and machine intelligence reinforce one another.